[China Tech] Local Doctors Develop AI Tool for Dental Health Management
China Tech is a column dedicated to the innovations reshaping China – and, inevitably, the world. From cutting-edge AI labs and next-gen robotics to homegrown apps that redefine daily life, we explore the breakthroughs that emerge from the country's relentless drive for technological dominance. Some are game-changers, others cautionary tales, but all offer a glimpse into the future as it's being built, at breakneck speed, in China.
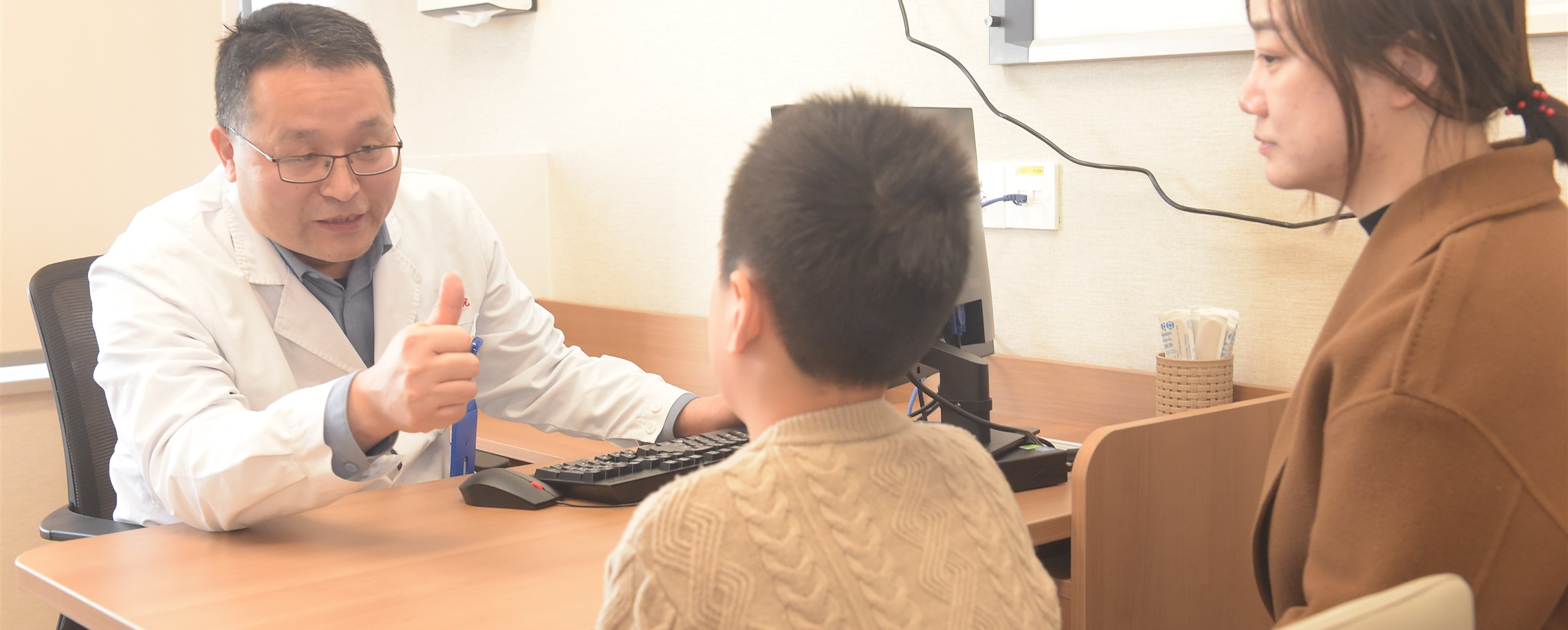
Local specialists have developed an AI-based screening tool for periodontal disease that achieves 94 percent accuracy and assists grassroots doctors.
Periodontal disease is a common chronic oral condition, often referred to as an "invisible killer" of teeth. Its early symptoms are subtle, but in later stages, individuals may experience tooth loosening and even loss, which can severely affect dental health.
Current diagnostic methods are invasive, time-consuming and heavily reliant on the doctor's experience.
Panoramic X-rays provide a widely accepted imaging technique that meets the need for broader screening.
To address this issue, Dr Maurizio S. Tonetti, from the innovation center for dental implantation at Shanghai Ninth People's Hospital, collaborated with scientists from Shanghai Tech University to develop an AI model capable of accurate diagnoses from panoramic X-rays.
![[China Tech] Local Doctors Develop AI Tool for Dental Health Management](https://obj.shine.cn/files/2025/11/26/a0307207-4330-49b8-9871-de20e243bfbf_0.jpg)
The tool has been developed using data from over 10,000 panoramic X-ray cases, validated by clinical diagnoses and the consensus of international experts.
It is the first AI model designed for periodontitis diagnosis utilizing panoramic X-rays and has undergone multi-center and multi-standard verification.
This research offers an effective, precise and promotable tool for periodontitis screening. With high-quality panoramic X-rays, doctors can conduct screenings without requiring patients to undergo uncomfortable and invasive procedures.
This approach is particularly beneficial for community health centers and remote areas with limited dental resources, enabling grassroots doctors to achieve efficient, widespread and accurate screenings.
The research has been published in Digital Medicine, which represents a major milestone in medical engineering.
In Case You Missed It...